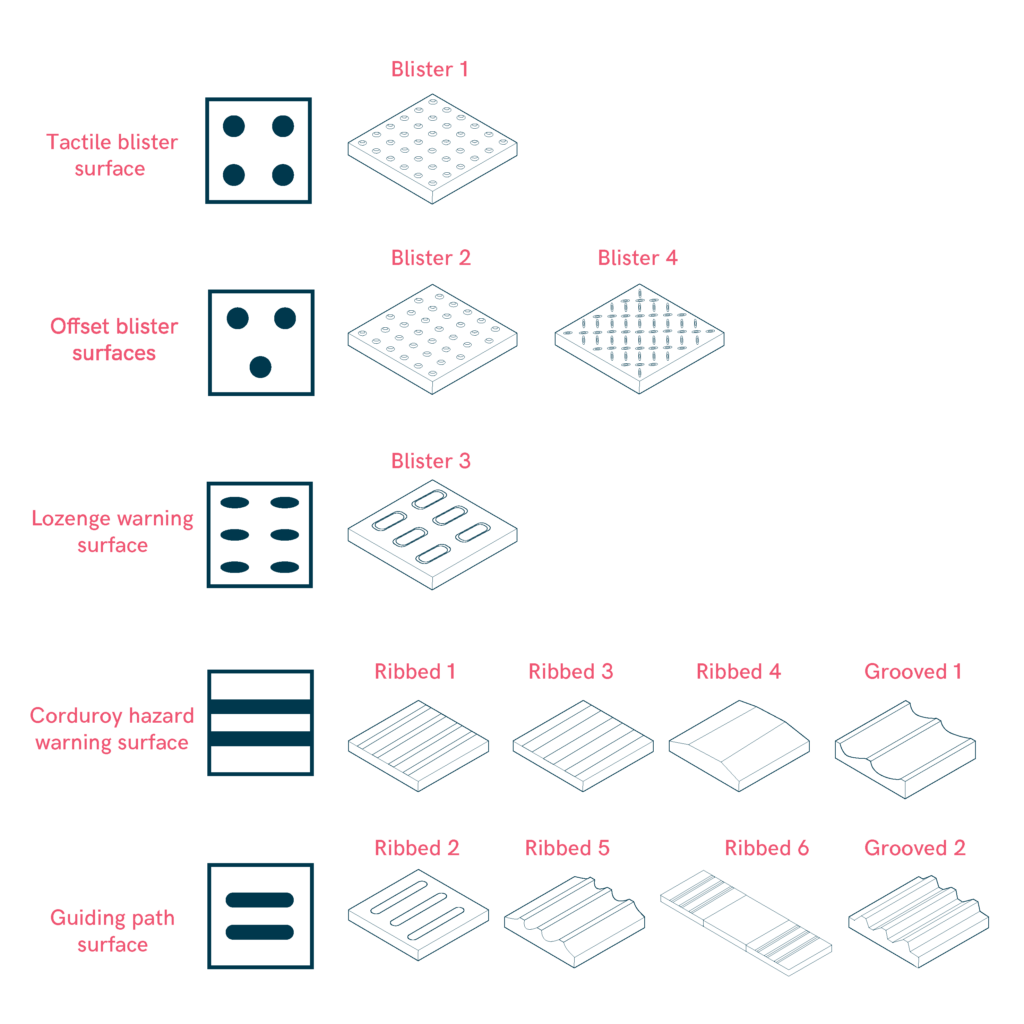
Tactile Flooring
Tactile flooring serves two key functions: hazard warning and orientation. It alerts users to dangers like stairs, crossings, or platform edges while guiding them where natural references are absent. Detection relies on sight, touch, and sound—high color contrast aids visibility, textured surfaces assist through foot contact or a cane, and a distinct sound provides auditory feedback. To maintain effectiveness, tactile flooring must be durable and resistant to wear and environmental exposure.
For clarity, adjacent surfaces should be smooth, with joint gaps no wider than 10 mm or deeper than 2 mm. Using slip-resistant materials ensures long-term safety. Regular maintenance prevents deterioration, preserving visibility and functionality. Properly implemented, tactile flooring enhances accessibility for visually impaired individuals.
- Use high color contrast to enhance visibility.
- Implement textured surfaces for tactile recognition via foot contact or a cane.
- Ensure the flooring produces a distinct sound for auditory feedback.
- Adjacent surfaces should be smooth for clear distinction.
- Keep joint gaps ≤10 mm wide and ≤2 mm deep to prevent obstruction.
- Use slip-resistant, durable materials to withstand wear and environmental factors.
- Regular maintenance is essential to prevent deterioration.
- Consider environmental exposure when selecting materials.
- Ensure the flooring remains functional and visible over time.
Sources
- https://www.une.org/encuentra-tu-norma/busca-tu-norma/norma?c=N0069408
- https://accessible-eu-centre.ec.europa.eu/content-corner/digital-library/en-172102021-accessibility-and-usability-built-environment-functional-requirements_en
- https://www.access-board.gov/adaag-1991-2002.html#2.%20GENERAL
- https://universaldesign.ie/built-environment/building-for-everyone/building-for-everyone-full-series
- https://www.codigotecnico.org/pdf/Documentos/SUA/DccSUA.pdf
- https://www.networkrail.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/NR-GN-CIV-300-06-Tactile-Paving-wayfinding.pdf
- https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/61df0c91e90e07037794fe90/guidance-on-the-use-of-tactile-paving-surfaces.pdf
- Carers
- Children
- Cognitive
- Cognitive abilities
- Decolonial perspective
- Digital
- Digital barrier
- Enviroment
- Environmental
- Gender and generations
- Gender perspective
- Hearing impairment
- Low-education
- Low-income
- Older people
- Other
- Physical abilities and features
- Sensory and Physical
- Socioeconomic
- Visual impairment