Safe Stair Mobility
Stair chairs are designed to provide seamless mobility for users navigating stairs. With adjustable seating, armrests, and footrests, these chairs allow for comfortable and safe travel. Ideal for slopes up to 40°, stair chairs feature rotating seats for easy boarding and disembarking. Equipped with safety belts, anti-shear devices, and emergency stop functions, they ensure secure use for individuals with mobility needs.
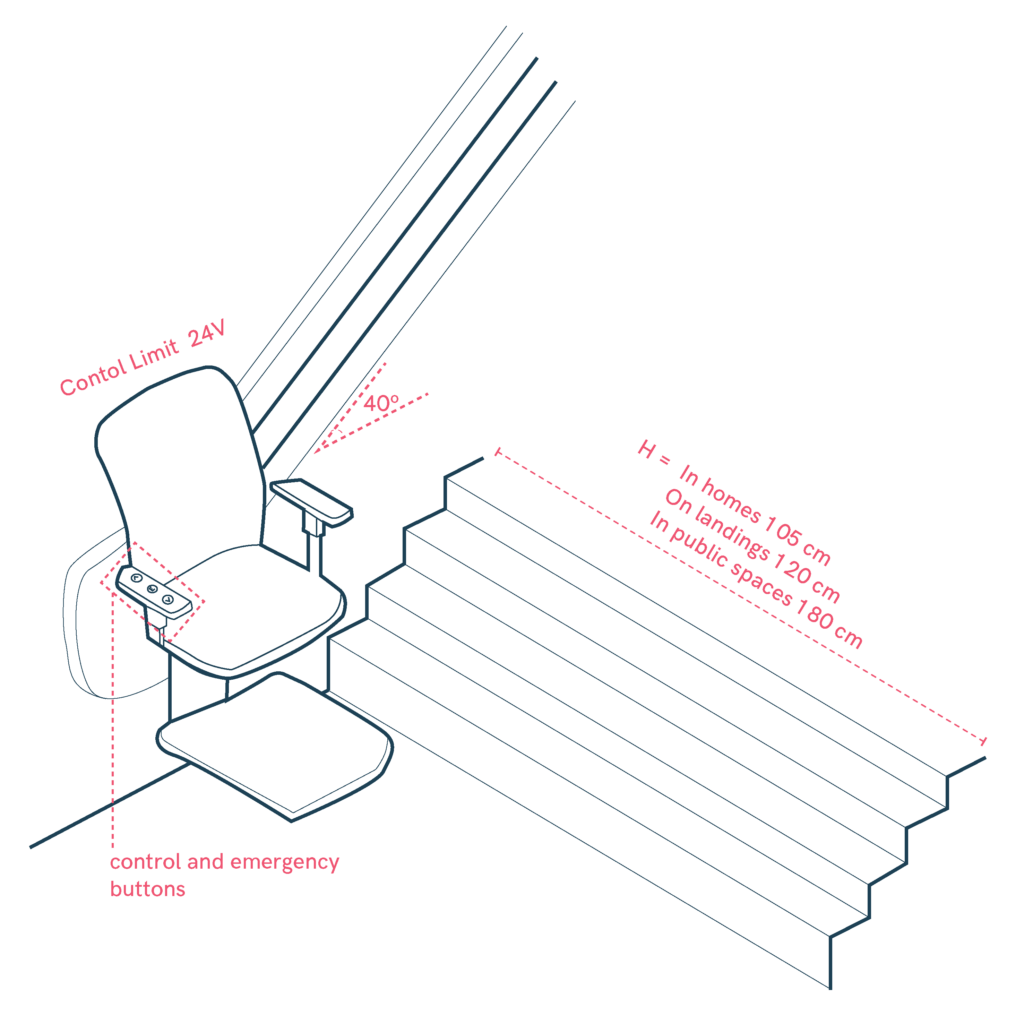
- Ergonomic seat with backrest, armrests, footrests, and safety belt for secure travel.
- Adjustable seat, armrests, and footrests for user comfort.
- Rotating seat (at least 90°) for easy boarding and alighting.
- Rail slope up to 40°, securely anchored and protected from indirect contact.
- Control voltage limited to 24V, with a minimum load capacity of 150 daN.
- Hydraulic transmission for straight paths; mechanical system for inclines, turns, and speed changes.
- Constant pressure controls on the armrest, easily accessible from the seat.
- Call and resend buttons available on each floor for user convenience.
- Electromagnetic brake ensures smooth stops, with manual operation in case of power failure.
- Safety features include anti-shear and anti-crush devices on the footrest.
- Chain traction models equipped with a brake system for slack or breakage.
- Emergency stop button for added safety.
- Minimum stair width: 105 cm in homes, 120 cm on landings, and 180 cm in public spaces.
- Where possible, separate circulation paths for chair users and pedestrians.
- Boarding areas designed for smooth access and wheelchair maneuverability.
Sources
- https://accessible-eu-centre.ec.europa.eu/content-corner/digital-library/en-172102021-accessibility-and-usability-built-environment-functional-requirements_en
- https://www.access-board.gov/adaag-1991-2002.html#2.%20GENERAL
- https://universaldesign.ie/built-environment/building-for-everyone/building-for-everyone-full-series
- https://www.codigotecnico.org/pdf/Documentos/SUA/DccSUA.pdf
- Carers
- Children
- Cognitive
- Cognitive abilities
- Decolonial perspective
- Digital
- Digital barrier
- Enviroment
- Environmental
- Gender and generations
- Gender perspective
- Hearing impairment
- Low-education
- Low-income
- Older people
- Other
- Physical abilities and features
- Sensory and Physical
- Socioeconomic
- Visual impairment