Acoustic Design
The acoustic design of spaces plays a crucial role in creating environments that are comfortable and functional for all users. Proper acoustic planning ensures clear communication, reduces distractions, and enhances the intended use of a space, whether it’s for speech, music, or other purposes. The following recommendations focus on optimizing acoustics in different areas of a building, from room placement to material selection and sound control.
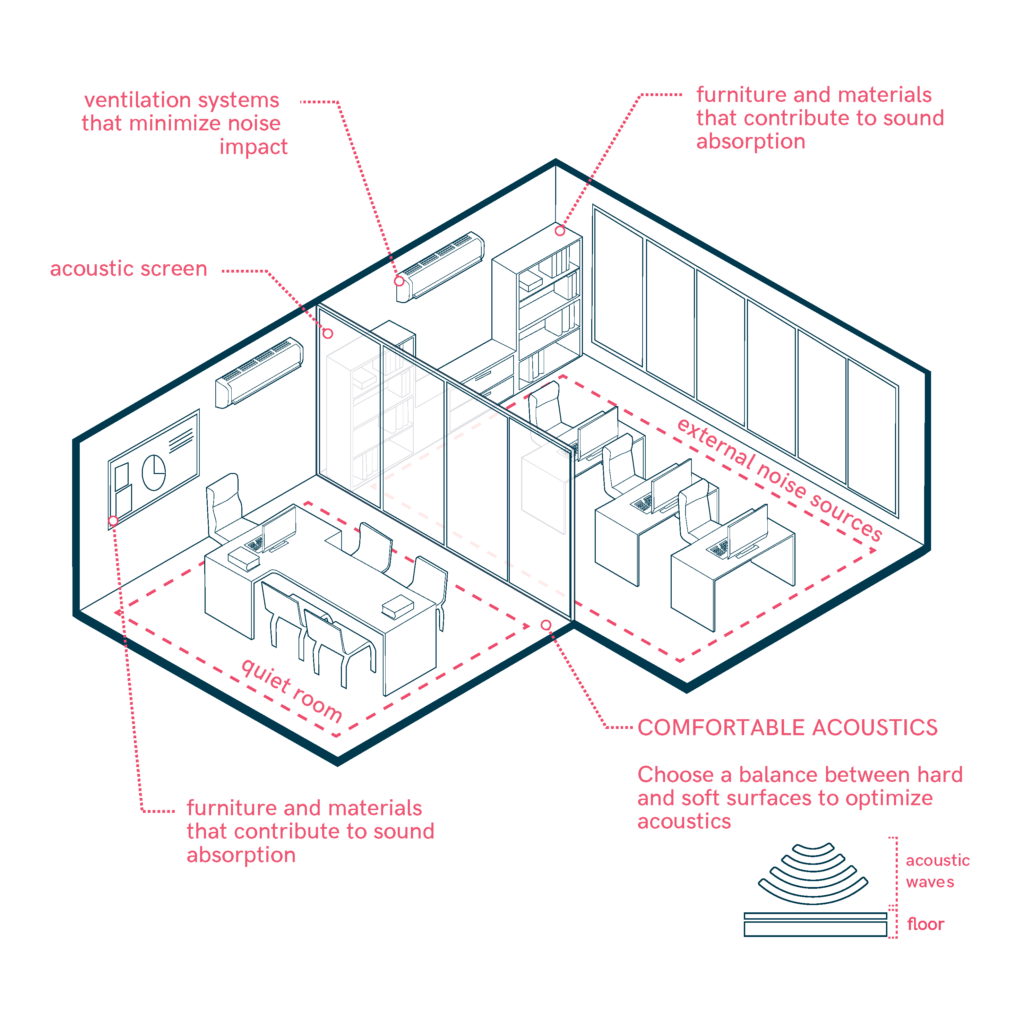
- Incorporate acoustic requirements into the design process from the earliest planning stage to ensure appropriate sound quality.
- Position quiet rooms, such as offices, meeting rooms, and prayer rooms, away from external noise sources to minimize disturbance.
- Use buffer zones like lobbies, foyers, or screens to separate quiet spaces from noisier areas, enhancing privacy and sound quality.
- Tailor the acoustic characteristics of each room to its intended use, adjusting reverberation time for speech, music, or other activities.
- Balance hard and soft surfaces in each room to achieve the desired reverberation time; consider absorptive materials like carpets or curtains for quieter rooms.
- Select finishes, furniture, and materials that contribute to sound absorption and prevent excessive noise reflection, such as mineral fiber tiles or soft upholstery.
- Install ventilation systems that minimize noise impact, ensuring a quiet environment while maintaining air quality and comfort.
Sources
- https://accessible-eu-centre.ec.europa.eu/content-corner/digital-library/en-172102021-accessibility-and-usability-built-environment-functional-requirements_en
- https://breeam.es/
- https://www.usgbc.org/leed
- https://evalore.es/servicio/certificaciones-medioambientales/
- https://www.codigotecnico.org/pdf/Documentos/SUA/DccSUA.pdf
- https://universaldesign.ie/built-environment/building-for-everyone/building-for-everyone-full-series
- Carers
- Children
- Cognitive
- Cognitive abilities
- Decolonial perspective
- Digital
- Digital barrier
- Enviroment
- Environmental
- Gender and generations
- Gender perspective
- Hearing impairment
- Low-education
- Low-income
- Older people
- Other
- Physical abilities and features
- Sensory and Physical
- Socioeconomic
- Visual impairment