Inclusive Mobility for People with Disabilities
Mobility solutions should address the needs of individuals with disabilities, ensuring they can navigate urban spaces with ease and confidence. By incorporating tactile paving, accessible tricycles, and well-maintained infrastructure, cities can foster inclusivity and equity in transportation.
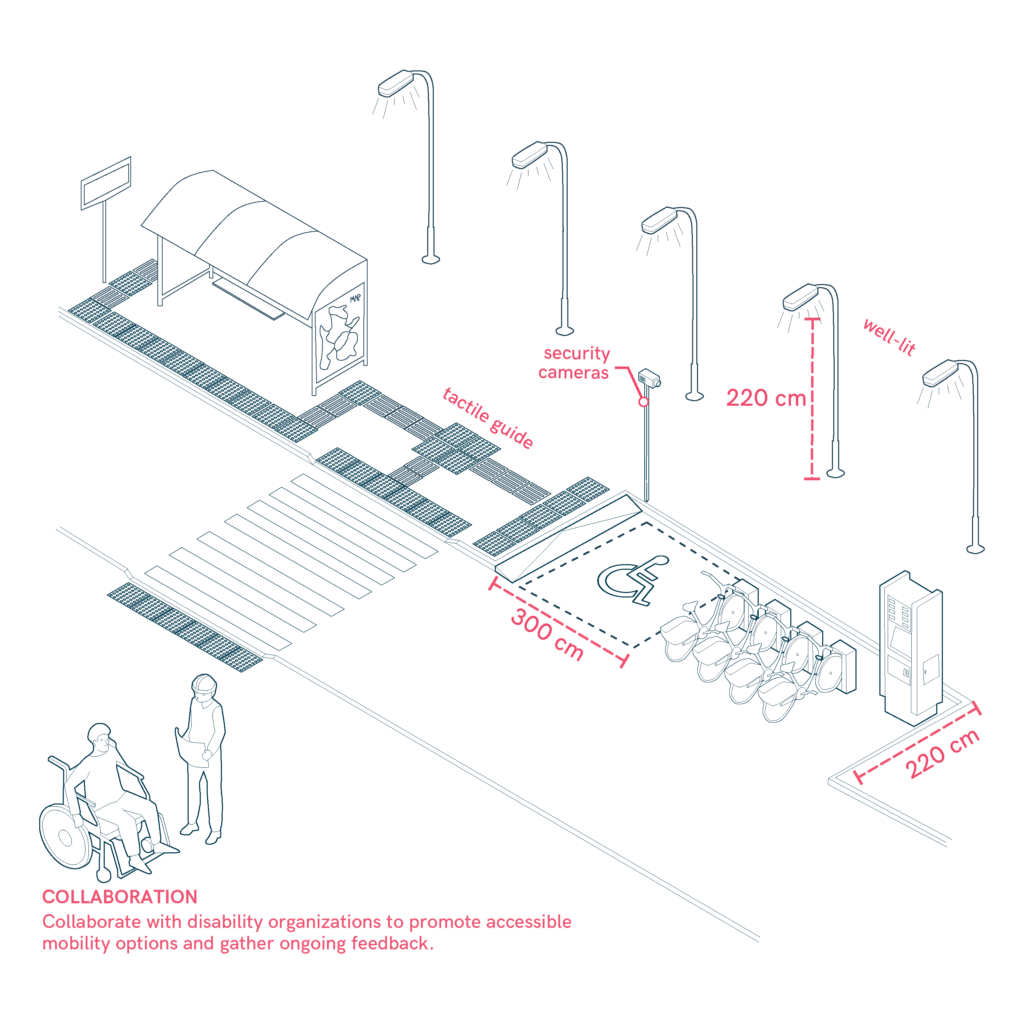
- Incorporate tactile paving and visual cues at PMV-pedestrian intersections for easy navigation.
- Ensure tricycles and mobility devices meet necessary safety standards, with dedicated parking spaces to enhance usability.
- Develop accessible infrastructure, such as ramps and sidewalks, to facilitate tricycle and mobility device use.
- Collaborate with disability organizations to promote accessible mobility options and gather ongoing feedback.
- Design stations that are accessible to people with disabilities, located near public transport, hospitals, and shopping centers. Include features like ramps, lighting, security cameras, and regular maintenance.
Sources
- https://accessible-eu-centre.ec.europa.eu/content-corner/digital-library/en-172102021-accessibility-and-usability-built-environment-functional-requirements_en
- https://www.iso.org/standard/71860.html
- https://www.t-l.ch/collectivites/guide-des-amenagements-pour-les-transports-publics-routiers-tl/
- https://www.leitfadenbarrierefreiesbauen.de/fileadmin/downloads/archiv/barrierefreies_bauen_leitfaden_en_bf_version2.pdf
- https://www.vitoria-gasteiz.org/http/wb021/contenidosEstaticos/especial/cea/20190917/Avance_PMSEP_2020_2030.pdf
- https://www.punt6.org/es/books/espacios-para-la-vida-cotidiana/
- Carers
- Children
- Cognitive
- Cognitive abilities
- Decolonial perspective
- Digital
- Digital barrier
- Enviroment
- Environmental
- Gender and generations
- Gender perspective
- Hearing impairment
- Low-education
- Low-income
- Older people
- Other
- Physical abilities and features
- Sensory and Physical
- Socioeconomic
- Visual impairment